Introduction to Immersive Training and XR
Immersive training refers to a modern approach to skill development and learning that leverages advanced technologies to create highly engaging, realistic simulations. This method allows individuals to perform tasks and practice skills in a safe and controlled environment, replicating real-world scenarios without the inherent risks associated with them. As industries evolve and the demand for highly skilled professionals increases, immersive training is becoming essential in enhancing workforce competency and readiness.
At the forefront of this innovative educational paradigm lies extended reality (XR), an umbrella term that encompasses various immersive technologies, including virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). Virtual reality offers fully immersive experiences through headsets that transport users into computer-generated environments, ideal for activities ranging from medical training to flight simulations. On the other hand, augmented reality overlays digital elements onto the real world, enabling learners to interact with both physical and virtual objects simultaneously. Mixed reality combines aspects of both VR and AR, allowing users to manipulate 3D holograms within their environment, thereby enhancing collaborative and teamwork exercises.
The growing importance of realistic training simulations driven by XR cannot be understated. Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and education are increasingly adopting these technologies to improve training outcomes significantly. By providing learners with practical experience in a risk-free setting, XR facilitates deeper learning retention and skill acquisition. As organizations strive for efficiency and effectiveness in workforce development, embracing immersive training methods becomes crucial for nurturing talent, fostering innovation, and ensuring industry-leading performance. With the rapid advancements in XR technology, the potential for transformative training experiences continues to expand, paving the way for more adaptive and responsive learning solutions across various sectors.
The Role of XR in Healthcare Training
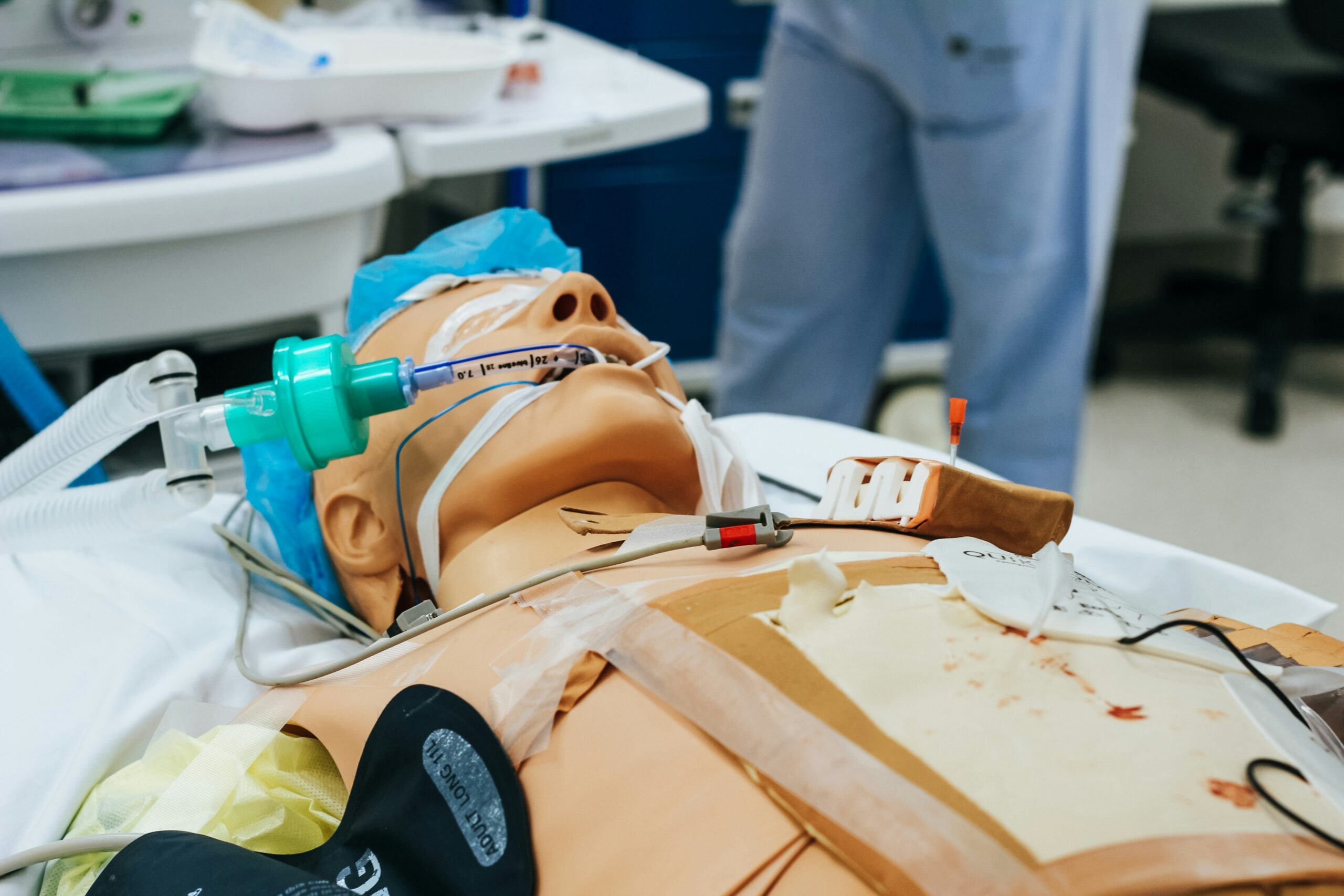
Extended Reality (XR), encompassing virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), has revolutionized healthcare training by providing immersive and interactive simulations. These technologies allow medical professionals to engage in realistic scenarios without the risks associated with traditional training methods. For instance, XR enables trainees to practice complex surgical procedures in a controlled virtual environment, fostering skill development and confidence before they operate on actual patients.
One significant advantage of XR in healthcare is the ability to simulate various medical emergencies and patient interactions. This interactive approach not only enhances the learning experience but also allows healthcare workers to manage pressure effectively while dealing with unexpected situations. By exposing trainees to a myriad of scenarios, XR can help refine decision-making skills and improve patient care outcomes. The immediate feedback provided during these simulations further reinforces learning and allows for continuous improvement.
Moreover, XR technology facilitates remote learning and collaboration among medical professionals. For instance, healthcare practitioners can immerse themselves in the same virtual environment, regardless of their physical location, enabling them to learn from one another and share insights effectively. This accessibility is particularly beneficial in rural or underserved areas, where specialized training may be limited.
In summary, the integration of XR in healthcare training is transforming how medical professionals acquire skills and knowledge. By leveraging the immersive and interactive capabilities of XR, healthcare training can address the complexities of real-life situations, ultimately leading to improved patient care and outcomes. As technology continues to advance, the role of XR in medical education is expected to grow, fostering a new generation of skilled healthcare providers equipped to meet the ever-evolving challenges of the industry.
XR Innovations in Medical Education
Extended Reality (XR), encompassing both Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), has significantly transformed the landscape of medical education. As the healthcare field continues to embrace technological advancements, XR tools provide new avenues for learning that enhance the educational experience for both students and instructors. One of the most notable innovations is the development of VR surgical simulators. These immersive platforms allow medical students to practice surgical techniques in a risk-free environment, thereby fostering skills and confidence before engaging in real-life situations. The ability to simulate complex procedures not only reduces potential errors in actual surgeries but also enables students to gain hands-on experience through repeatable practice.
In addition to surgical training, AR anatomy visualization tools have emerged as vital resources in medical education. These tools project interactive 3D models of anatomical structures onto physical cadavers or students’ physical surroundings, providing learners with a richer understanding of human anatomy. By integrating digital elements with the real world, AR enhances students’ spatial awareness and comprehension of complex bodily systems. This juxtaposition of virtual elements with physical entities offers a dynamic way to engage with course material, which contrasts sharply with traditional methods of rote learning that often rely on textbooks or static images.
The effectiveness of these XR innovations lies not just in engagement but also in tangible outcomes. Studies have shown that students utilizing VR and AR technologies exhibit improved retention and performance compared to those engaged with conventional teaching methodologies. The immersive nature of XR fosters an experiential learning environment conducive to better understanding. As educational institutions progressively adopt such technologies, they are likely to witness a paradigm shift in the way medical education is imparted, ultimately leading to enhanced competency among future healthcare professionals.
Case Studies: Successful XR Healthcare Training Programs
The integration of Extended Reality (XR) in healthcare training has been met with immense enthusiasm and success across various medical institutions. For instance, the University of Illinois at Chicago has pioneered a program whereby medical students are immersed in a simulated environment that mimics real-life scenarios. This approach allows students to practice complex surgical procedures in a risk-free setting. By using XR technology, these students can visualize anatomy in three dimensions and manipulate virtual organs to comprehend surgical techniques more intimately. This experiential learning significantly enhances their confidence and skill set before entering the operating room.
Another exemplary case is the partnership between Stanford Medicine and Osso VR, a virtual reality training platform. This collaboration resulted in the development of a comprehensive curriculum for orthopedic procedures. The immersive simulations offer healthcare professionals a chance to refine their skills, making mistakes in a controlled environment without real-world consequences. As a result, participants report heightened preparedness and improved performance when applying their skills in actual surgeries. Furthermore, Osso VR’s analytics capabilities score performance during simulations, thereby identifying areas needing improvement for continuous professional development.
In a different application of XR, the Cleveland Clinic implemented a mixed-reality program for nursing staff. This initiative utilizes Microsoft’s HoloLens to overlay digital information onto physical patient scenarios. By enabling nurses to visualize patient data and medical information in their line of sight, the program streamlines workflow and enhances decision-making processes. Feedback from participants indicated that this method not only improved clinical skills but also fostered better communication among team members during patient care.
These case studies collectively illustrate the transformative effects of XR in healthcare training. The shift from traditional learning modalities to immersive experiences has led to enhanced skills acquisition, improved patient outcomes, and greater confidence among healthcare professionals. By adopting XR technologies, medical institutions are not only keeping pace with technological advancements but are also redefining the future of healthcare education.
The Impact of XR on Manufacturing Training
Extended Reality (XR) technologies are making significant strides in the realm of manufacturing training, revolutionizing how workers acquire skills and knowledge essential for their job functions. Traditional training methods often involve theoretical approaches that may lack practical application. However, through XR, employees can engage in interactive, immersive experiences that facilitate a deeper understanding of complex processes. This technology combines augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to create rich training environments where workers can practice tasks without the risks associated with real-world scenarios.
One of the primary benefits of XR in manufacturing training is the ability to simulate machinery operations and safety protocols in a controlled setting. This allows employees to familiarize themselves with equipment and procedures before handling real tools or machinery, ultimately reducing the possibility of errors and accidents. For example, XR can guide trainees through troubleshooting processes, enabling them to learn from mistakes without the consequences that would occur in a physical environment. As a result, the onboarding process becomes more efficient, enhancing skill acquisition and retention.
Moreover, XR environments can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a manufacturing facility. Training programs can incorporate a variety of scenarios that employees may encounter on the job, preparing them for real-world applications. These experiences can range from routine tasks to emergency situations, providing comprehensive preparation for workers. Additionally, XR training can be updated rapidly to reflect changes in industry standards or equipment, ensuring that employees always receive current information and techniques.
In conclusion, the impact of XR on manufacturing training is profound. By providing hands-on engagement in a risk-free environment, this technology not only enhances skills and safety protocols but also fosters a culture of continuous learning within organizations. As industries continue to evolve, embracing XR for training is likely to become a standard practice, fundamentally transforming workforce development in the manufacturing sector.
Using XR for Equipment Training
In recent years, extended reality (XR) technologies, which encompass virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), have gained traction in various industries, especially concerning equipment training. This innovative approach allows employees to engage with virtual models of complex machinery safely, enhancing their understanding of operational functions without the risks associated with real-world equipment.
One of the most significant advantages of XR in equipment training is its ability to provide immersive and interactive experiences. Trainees can manipulate virtual models, simulating real-life scenarios where they can practice critical skills. This interactivity fosters a deeper comprehension of equipment functionalities and safety protocols. Additionally, XR can incorporate elements of gamification, transforming the learning process into an engaging experience that encourages participation and improves knowledge retention.
The integration of XR for training purposes also addresses scalability issues. Organizations can provide standardized training modules that can be accessed by employees across various locations, ensuring uniformity in knowledge acquisition. Furthermore, XR training modules can be updated easily, allowing organizations to adapt quickly to new equipment or safety regulations without incurring the costs associated with traditional training methods, such as live demonstrations or physical simulations.
Another notable benefit is the reduction in training time. XR experiences can accelerate the learning curve, as employees are equipped with the necessary skills to operate complex machinery in a fraction of the time compared to conventional training methods. By allowing individuals to practice and refine their skills in a risk-free environment, XR contributes not only to employee confidence but also to overall operational efficiency.
Overall, utilizing XR for equipment training is a transformative approach that modernizes how organizations prepare their workforce. As industries continue to evolve, XR technologies will likely play an increasingly pivotal role in enhancing training frameworks, thereby improving safety and productivity in the workplace.
Benefits of XR Training in Manufacturing
Extended Reality (XR) technologies are revolutionizing manufacturing training by providing innovative solutions that enhance learning outcomes and operational efficiency. One of the most significant advantages of XR training is the increased retention rates among employees. Traditional training methods often result in information overload, leading to poor knowledge retention. In contrast, immersive XR environments allow trainees to engage in hands-on activities and realistic simulations, which facilitate better understanding and memory retention. This active learning approach is particularly beneficial in complex manufacturing processes, where practical experience is essential.
Furthermore, XR training offers a substantial reduction in overall training costs. Traditional training often requires physical resources, including equipment and facilities, as well as travel expenses for on-site training sessions. XR training eliminates many of these costs, as employees can participate in training from various locations without the need for physical tools or extensive materials. With cloud-based XR applications, updates and new training modules can be deployed swiftly, ensuring that all employees have access to the latest information without incurring additional expenses. This makes XR an economically viable option for employers.
Another critical benefit of XR training in the manufacturing sector is the enhancement of safety standards through hazard simulations and improved situational awareness. XR environments can recreate hazardous scenarios that workers may encounter in the manufacturing process, allowing them to practice appropriate responses without real-world risks. This not only prepares trainees for actual situations they will face but also fosters a culture of safety within the workplace. By increasing workers’ awareness of potential hazards, companies can significantly reduce accidents and related costs, contributing to a safer and more efficient work environment.
Military Applications of XR Training
Extended Reality (XR), which encompasses virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), is making significant strides in military training environments. One of the primary advantages of XR technologies is their ability to create immersive virtual scenarios that closely mimic real-life battlefield conditions. This capability enables soldiers to engage in complex tactical training exercises without the attendant risks associated with actual combat situations.
By utilizing XR, the military can replicate various operational environments, terrains, and challenges that soldiers might encounter. For instance, soldiers can practice in dense urban settings, arid deserts, or even at sea, all built within a controlled virtual environment. This simulation not only enhances their tactical skills but also allows for the rehearsal of critical decision-making processes under pressure. Furthermore, XR training can incorporate real-time data and analytics, providing soldiers with instant feedback on their performance.
The implementation of XR in military contexts also addresses logistical challenges associated with conventional training methods. Traditional simulations may require significant resources, including physical equipment and personnel, to create a realistic training environment. Conversely, XR systems offer a more resource-efficient solution, allowing multiple soldiers to train concurrently within diverse scenarios and frameworks without the need for extensive outdoor setups.
Moreover, the controlled nature of XR training enables the embedding of ethical decision-making and mental health assessments. Soldiers can confront moral dilemmas and psychological stressors in a simulated setting, preparing them for the emotional and cognitive challenges of real combat. This training can lead to better preparedness and resilience when faced with high-stress situations on the battlefield.
As military organizations continue to adopt these advanced technologies, XR is set to redefine the boundaries of training, providing soldiers with innovative tools that enhance their readiness and effectiveness in increasingly complex operational environments.
VR Simulations for Combat Readiness
Virtual Reality (VR) simulations have emerged as a transformative tool within military training, particularly for enhancing combat readiness. These immersive environments enable military personnel to engage in lifelike scenarios, improving their decision-making skills and crisis management capabilities. By replicating the complexities of modern warfare, VR allows soldiers to experience and respond to various combat situations without the risks associated with real-life training exercises.
The development of virtual combat environments leverages cutting-edge technology to create realistic settings that can simulate a wide range of battle conditions. These simulations incorporate detailed graphics, tactical challenges, and environmental factors, all designed to replicate what soldiers may encounter on the battlefield. This fidelity to real-world scenarios helps trainees to develop a clear understanding of operational dynamics, allowing them to hone their skills in a safe yet challenging environment.
Moreover, VR simulations for combat readiness serve as valuable tools for improving teamwork and communication among units. Participants can interact and react in real-time within these virtual spaces, reinforcing critical collaborative skills essential for mission success. The ability to debrief and analyze performance after simulations further enhances learning outcomes, enabling trainees to identify areas for improvement and apply lessons learned to future scenarios.
Ultimately, the integration of VR technology into military training programs not only bolsters individual soldier preparation but also enhances overall unit effectiveness. As these virtual environments evolve, they will likely play an increasingly significant role in shaping the way military forces train for combat, ensuring they are better equipped to face the challenges ahead. This innovative approach to training exemplifies how technology can lead to more adept and prepared personnel in a rapidly changing operational landscape.
Collaborative Training in XR for Military Units
Extended Reality (XR) technology is revolutionizing collaborative training methods within military units, offering immersive environments where personnel can engage and practice together, regardless of geographical constraints. Through XR, military training transcends traditional physical limitations, enabling soldiers to participate in shared virtual spaces that simulate combat scenarios and tactical exercises. This capability enhances the ability to cultivate teamwork, improve communication, and develop strategies in real-time.
Unlike conventional training, where teams might be restricted to drills and maneuvers in physical locations, XR experiences provide flexibility and versatility. Soldiers can interact in a rich virtual landscape, enabling them to rehearse tactics while working on their cohesion as a unit. This dynamic setup fosters a greater understanding among team members, as they can visualize strategic positions, assess threat patterns, and refine their decision-making processes collaboratively. Realistic avatars represent each participant, allowing for an authentic sense of presence and engagement within the training platform.
Moreover, the collaborative nature of XR training tools facilitates the incorporation of diverse perspectives. Different roles within military units can be simulated in these environments, ensuring that personnel experience each aspect of a mission. This multifaceted approach not only boosts individual capabilities but also strengthens inter-departmental relationships, as soldiers learn to rely on one another’s skills and expertise. Additionally, data collected during these training sessions can offer valuable insights into each soldier’s performance, identifying areas for improvement and promoting adaptive learning strategies within the unit.
As the military sector continues to embrace XR technologies, the evolution of collaborative training approaches is expected to significantly contribute to operational effectiveness and preparedness. By harnessing the power of XR, military units can ensure that they are not only well-trained but also strategically aligned, creating a formidable team capable of navigating complex operational landscapes.
Advantages of XR over Traditional Training Methods
Extended Reality (XR) training methods present numerous advantages over traditional training approaches, primarily through their ability to provide cost-effective, accessible, and engaging educational experiences. One of the most significant benefits of XR lies in its cost-effectiveness. Traditional training often requires extensive materials, travel expenses for instructors, and the maintenance of physical training facilities. In contrast, XR enables organizations to create virtual environments that eliminate these additional costs. This shift not only reduces financial burdens on organizations but also maximizes resource allocation for other critical areas.
In terms of accessibility, XR training breaks down geographical barriers, allowing learners from various locations to engage with training content. Whether through virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR), individuals can access training modules from anywhere in the world, creating an inclusive learning environment. This availability is especially crucial in industries where on-site training may not be feasible due to logistical challenges or health guidelines.
Furthermore, XR training methods offer superior flexibility in scheduling. Traditional training often necessitates time-consuming coordination between participants and instructors, limiting opportunities for on-demand learning. XR, however, allows learners to progress at their own pace, choosing when and how they wish to engage with training materials. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for adult learners who balance professional commitments alongside their educational pursuits.
Lastly, the inherent nature of XR promotes enhanced learner engagement. By immersing participants in realistic simulations and interactive scenarios, XR captures attention and fosters active participation. Such experiences facilitate deeper understanding and retention of knowledge compared to passive learning methods often employed in traditional training. In conclusion, the advantages offered by XR in terms of cost-effectiveness, accessibility, flexibility, and engagement mark a significant evolution in training methodologies, making them a valuable asset across various industries.
Barriers to Implementing XR Training
The incorporation of Extended Reality (XR) training solutions into organizational settings is a progressive shift. However, various challenges hinder its widespread adoption. One of the primary barriers is the associated costs. Organizations often need to invest significantly in hardware and software to deploy XR training effectively. This initial investment can be a deterrent, especially for smaller enterprises with limited budgets. Additionally, businesses must consider the ongoing costs related to maintenance, updates, and potential scalability of the technology as their training needs evolve.
Another critical challenge relates to technological limitations. Not all organizations possess the necessary infrastructure to support XR systems. High-speed internet, advanced computing capabilities, and compatible hardware are essential for efficient implementation. In many instances, existing systems may require extensive upgrades, which can further escalate costs and complicate the implementation process. Furthermore, as XR technology continues to evolve, organizations must remain vigilant about integrating the latest advancements, which can be both time-consuming and challenging.
The need for trained personnel is another significant barrier. Although XR training solutions can enhance learning outcomes, their effective implementation often requires skilled professionals who understand both the technology and how to utilize it in training contexts. Organizations may face difficulty in recruiting or training staff with the specialized skills necessary to manage XR systems. This shortage can result in ineffective deployment of XR training initiatives, ultimately undermining their potential benefits.
Ultimately, while the advantages of XR training are compelling, organizations must navigate several barriers, including financial implications, technological readiness, and personnel training. Addressing these challenges is crucial for a smoother transition into adopting these innovative training solutions.
Future of XR in Training Solutions
As industries continuously evolve in response to technological advancements, the potential of Extended Reality (XR) in training solutions is expected to grow exponentially. XR encompasses Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR), providing immersive experiences that conventional training methods cannot match. The future of XR in training promises to enhance learning experiences, making them more interactive, engaging, and productive.
One significant trend in XR training solutions is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) integration. By combining XR with AI, training programs can become more adaptive, offering personalized experiences that cater to individual learner needs. Such tailored training can improve retention and skill acquisition, leading to higher proficiency in specific tasks and reducing the time required for new employees to become productive. Additionally, machine learning algorithms can analyze user data to continually refine XR training modules, ensuring they remain relevant and effective.
Another key forecast involves expanding accessibility to XR technologies. As hardware costs decrease and software solutions become more user-friendly, organizations across various sectors will likely adopt XR for training purposes. The increasing availability of XR devices, such as affordable VR headsets, will enable diverse industries—ranging from healthcare to manufacturing—to utilize these immersive training methods. This democratization of technology will allow companies of all sizes to enhance their training programs, fostering a culture of continuous learning.
Moreover, advancements in 5G technology will facilitate more robust and real-time XR experiences. With higher bandwidth and lower latency, trainees will be able to engage in more complex simulations and collaborative training sessions with peers from different geographic locations. This capability not only enhances engagement but also promotes teamwork and communication skills, crucial components of effective training.
Ultimately, the future of XR in training solutions appears promising. As advancements materialize and become more integrated into organizational frameworks, businesses will be better positioned to create a skilled workforce, equipped to meet the challenges of an ever-changing landscape.
Industry-Specific XR Training Tools
Extended Reality (XR) is redefining the training landscape across various industries through tailored tools that address unique sector needs. In the healthcare sector, for instance, virtual reality (VR) simulations enable medical professionals to practice surgical techniques in a risk-free environment. Tools such as Osso VR provide immersive training modules that enhance the learning experience, allowing practitioners to engage with 3D models of anatomy and refine their skills before encountering real-life scenarios.
In manufacturing, XR tools like PTC’s Vuforia offer augmented reality (AR) solutions that improve workforce efficiency. This technology superimposes digital information onto physical components, guiding operators during assembly or maintenance tasks. By utilizing such tools, organizations can reduce error rates and improve the overall training process, ensuring that employees acquire hands-on experience without the associated risks of operating heavy machinery. Interactive platforms empower workers to troubleshoot procedures and elevate their technical skills through immediate, context-driven feedback.
The military, too, benefits from XR training tools that simulate combat environments and complex tactical scenarios. Technologies such as the Synthetic Training Environment (STE) allow soldiers to train collaboratively in virtual landscapes that mimic real-world conditions. This immersive training fosters teamwork and decision-making skills while preparing personnel for the challenges they may face on the battlefield. Notably, these scenarios can be adjusted dynamically to introduce unexpected variables, enhancing adaptability and readiness in service members.
Additionally, the education sector presents opportunities for XR training tools that facilitate experiential learning. Institutions are increasingly incorporating AR and VR to create engaging lessons that promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills among students. As industry-specific XR training tools continue to evolve, they are becoming pivotal in bridging the skills gap across various fields, making training more effective and accessible.
Learner Engagement in Immersive Training
Immersive training experiences utilizing extended reality (XR) technologies are shifting how organizations approach learning and development. By creating interactive environments that simulate real-world scenarios, XR enhances learner engagement significantly compared to traditional training methods. This heightened engagement is crucial as it directly correlates with increased retention of information and skills. When learners participate in realistic simulations, they are not just passive recipients of knowledge but active participants who can make decisions in a safe, controlled environment.
The immersive nature of XR training allows learners to explore and interact with their surroundings, fostering curiosity and facilitating experiential learning. For instance, a medical professional can practice surgical procedures in a virtual operating room, providing a risk-free opportunity to hone their skills. This form of experiential learning is particularly impactful, as learners remember over 75% of what they practice compared to mere observation. Additionally, learners are more likely to remain engaged when they understand the relevance of their training to their real-life tasks and responsibilities.
Furthermore, XR technologies can cater to individual learning styles, allowing users to engage with content in a manner that suits them best. When learners have control over their training environment, they can take their time to explore, ask questions, and revisit scenarios, thereby enhancing comprehension and mastery. Interactive features, such as gamified elements within XR training, can also boost motivation and competitiveness among participants, leading to a more enthusiastic learning atmosphere.
In conclusion, the integration of XR in training practices significantly fosters learner engagement. By offering interactive, immersive experiences that closely resemble real-world scenarios, organizations not only create a more effective training process but also empower their workforce with the skills necessary to excel in their fields.
Measuring the Effectiveness of XR Training
As organizations increasingly adopt extended reality (XR) in their training programs, it becomes essential to evaluate the effectiveness of these immersive training experiences. Measuring the success of XR training is not only crucial for ensuring a return on investment but also for enhancing learning outcomes. Various metrics can be utilized for this purpose, providing insights into the strengths and areas for improvement in training methodologies.
One of the primary metrics for assessing XR training effectiveness is skills retention. Organizations often conduct follow-up assessments to determine how well trainees retain the skills learned through immersive experiences over time. Studies have shown that XR training can significantly enhance long-term retention compared to traditional methods, as it engages learners in a more interactive environment, enabling deeper cognitive processing.
Assessment scores also serve as a key indicator of XR training effectiveness. Organizations can implement a combination of pre- and post-training assessments, measuring knowledge acquisition and skill application. An improvement in assessment scores after XR training sessions indicates a higher level of understanding and competence in the relevant skills or knowledge areas.
Trainee feedback is another critical component in measuring the success of XR training programs. This can involve surveys, interviews, or focus groups, allowing participants to express their thoughts on the training experience, the relevance of the content, the level of engagement, and overall satisfaction. Collecting qualitative and quantitative feedback helps organizations gauge the trainees’ perspectives and experiences and identify areas where the training can be further improved.
Incorporating these metrics allows organizations to create a comprehensive evaluation framework for their XR training initiatives. This data-driven approach enables continuous improvement of training strategies, ensuring that immersive experiences effectively equip individuals with the skills they need to succeed in their respective roles.
Best Practices for Implementing XR in Training
As organizations begin to explore the potential of extended reality (XR) in their training programs, it is essential to adhere to best practices that facilitate a seamless integration of this technology into existing frameworks. The implementation process should be methodical, ensuring that the unique benefits of XR are realized while minimizing disruption.
First and foremost, a thorough needs assessment should be conducted to identify training gaps and objectives. This assessment allows organizations to understand which areas can benefit most from XR technologies, ensuring that investments are directed towards the most impactful solutions. It is vital to involve stakeholders from various departments, including learning and development, IT, and end-users, in this process. Such collaboration promotes a more comprehensive understanding of training needs and paves the way for more effective XR applications.
Next, organizations should invest in pilot programs that explore XR’s capabilities in a controlled setting before full-scale implementation. These pilot programs offer valuable insights into the functioning of XR technologies within a specific training context, enabling organizations to refine their approach. During this phase, feedback from participants is crucial. Continuous iterations based on participant experiences enhance the training experience and ensure that the technology genuinely meets the learners’ needs.
Furthermore, it is imperative to ensure that the acquired XR solutions are compatible with existing learning management systems and infrastructure. A well-structured technical integration plan reduces potential challenges and streamlines the deployment process. Additionally, organizations should provide adequate training for trainers and participants alike, ensuring that everyone is comfortable and proficient with the new technologies.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively integrate XR into their training frameworks, ultimately enhancing learning experiences and outcomes while fostering a culture of innovation and adaptability.
Ethical Considerations in XR Training
The integration of extended reality (XR) in training environments raises several ethical considerations that must be thoroughly examined. One of the foremost issues is data privacy. XR training systems often collect and process large amounts of personal data, including biometrics, behavioral responses, and performance metrics. This information can be sensitive, making it imperative for organizations to implement robust data protection measures. Ensuring compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is essential to safeguard trainees’ personal information and uphold their privacy rights.
Another critical ethical consideration pertains to the realism of simulations within XR training. Realistic scenarios can enhance learning outcomes; however, they also carry the risk of desensitizing users to certain experiences or situations. For instance, immersive training in high-stakes environments, such as military or emergency response training, could potentially lead to emotional detachment or a sense of invulnerability among participants. Ethical training design must thus strike a balance between realism and the psychological well-being of the trainee.
Furthermore, the psychological impacts of XR experiences are a significant concern. Extended exposure to realistic simulations could lead to unintended consequences, such as anxiety, disorientation, or post-traumatic stress for some individuals. These effects necessitate careful consideration of the content and context of training programs, as well as the provision of adequate support mechanisms for users who may find certain experiences distressing.
In essence, as organizations increasingly adopt XR technologies for training purposes, they must address these ethical issues to ensure that the deployment of such innovations is responsible, respectful, and conducive to a positive learning environment. Responsible practices will promote trust and acceptance of XR technologies in various industries while safeguarding the interests and welfare of users.
Conclusion: The Future Landscape of Training with XR
As the exploration into immersive training experiences continues to unfold, it is evident that Extended Reality (XR) holds substantial transformative potential across various industries. The integration of XR technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), into training frameworks offers unique advantages, including enhanced engagement, improved retention of knowledge, and the ability to simulate real-world scenarios without associated risks. These benefits make XR a compelling option for organizations aiming to modernize their training methodologies.
One of the fundamental shifts that XR introduces to training is the ability to provide a hands-on learning experience. Traditional training often relies on passive learning techniques, which may fall short in equipping employees with the skills required for complex tasks. XR, on the other hand, immerses learners in interactive environments, enabling them to practice and hone their skills in a safe yet realistic setting. This approach not only accelerates skill acquisition but also fosters a deeper understanding of job functions, which is crucial in fast-paced industries.
Furthermore, the adaptability of XR solutions means they can be tailored to meet specific training needs, making them valuable resources in sectors ranging from healthcare to manufacturing. However, to leverage the full potential of XR, organizations must commit to continuous innovation and embrace emerging technologies. Staying ahead in the rapidly evolving landscape of training technology is essential for leaders who aim to equip their teams with the necessary tools to thrive amidst changing job requirements.
In conclusion, XR is reshaping the future of training by offering immersive, interactive experiences that enrich the learning process. As organizations invest in these technologies, they will likely find significant improvements in employee performance and overall productivity. The journey towards fully harnessing XR’s capabilities represents not only a challenge but also an opportunity to redefine how training is perceived and implemented in the modern workforce.